GNSS STUDIES
GNSS* studies aim to define and evaluate innovative geolocation and navigation algorithms:
- Baseband signal processing
- Integrity, accurate position tracking and sensor hybridisation algorithms
- GNSS vulnerability (multipath, interference, spoofing, scintillation)
- Performance assessment in the laboratory and in real-life conditions

Signal processing algorithms (baseband)
The properties of the signals sent out by new constellations such as Galileo allow to improve geolocation performance and to strengthen the measurements provided by GNSS receivers. This opens the way to new applications, not only in the field of transport but also for science.

Integrity, accurate position tracking and sensor hybridisation
In order to improve geolocation performance and, in particular, integrity, the GNSS is completed with other sensors. Therefore GNSS hybridisation with inertial, odometric or visual sensors is essential to meet the requirements of future applications. In addition, accurate geolocation techniques such as RTK and PPP allow to achieve centimeter accuracy.

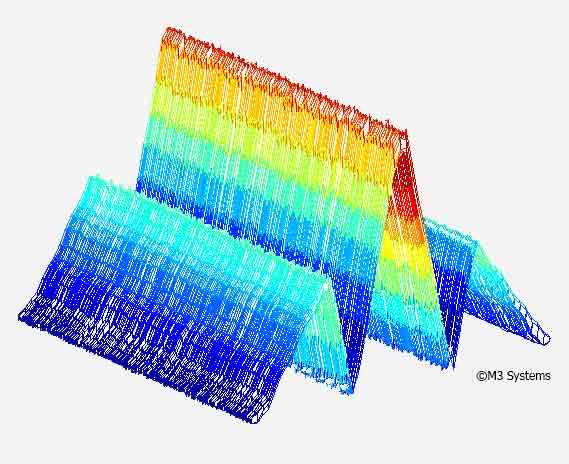
Vulnerability and mitigation algorithms
“In closed-in environments, cities for example, the GNSS signal is subject to interference due to its very low power and multipaths and which requires specific processing. Moreover, the analysis and mitigation of sources of interference, as well as the detection of spoofing, become indispensable in order to protect applications.”
REFERENCES
PROJECT
PROJECT
CLIENTS